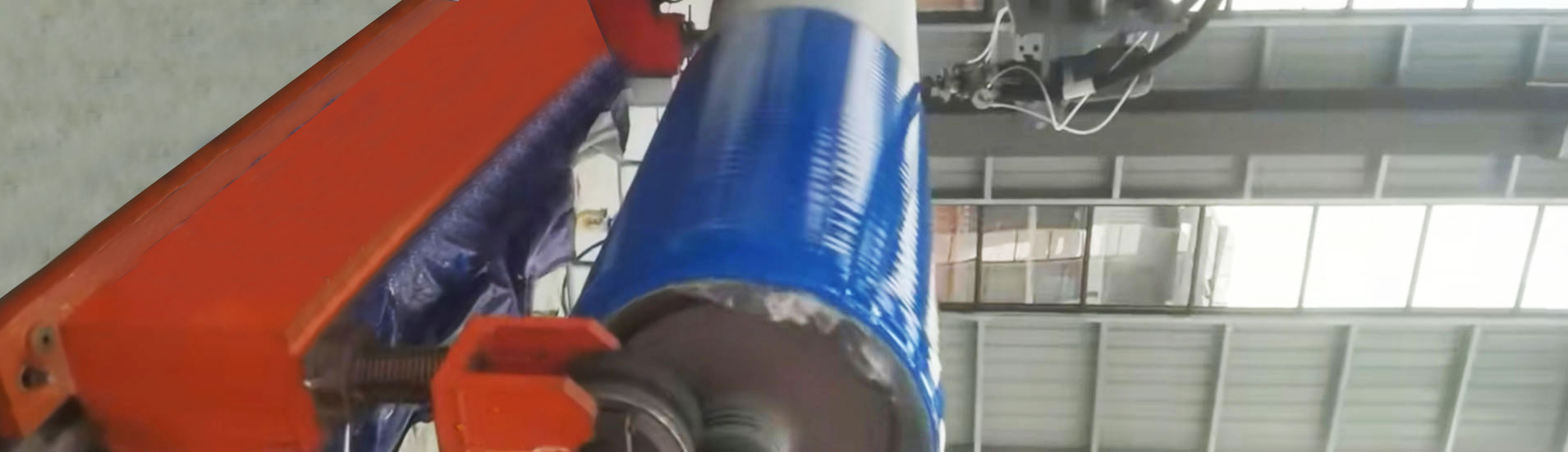
Rotational Casting Polyurethane-Rotomolding
Rotational casting is a slow, multi-axis rotation process where liquid or powdered polyurethane is placed in a mold, which then rotates around two or more axes at low speeds. Unlike centrifugal casting, which uses high-speed centrifugal force, rotational casting relies on gravity and rotation to coat the mold evenly.
It is ideal for complex, hollow shapes, large parts, or products with metal cores (e.g., rollers, wheels, and custom components). The process ensures even wall thickness and can produce parts without seams or welds.
Key Difference Between Rotational and Centrifugal Casting
| Feature | Centrifugal Casting | Rotational Casting |
| Rotation | High-speed, single axis | Low-speed, multi-axis |
| Force | Centrifugal force | Gravity + rotation |
| Ideal For | Sheets, squeegees, thin-wall tubes | Hollow parts, rollers, core-bonded components |
| Wall Thickness | Uniform but thin | Can be thick or variable, follows gravity |
| Air Bubbles | Eliminates | Can be controlled but slower curing |
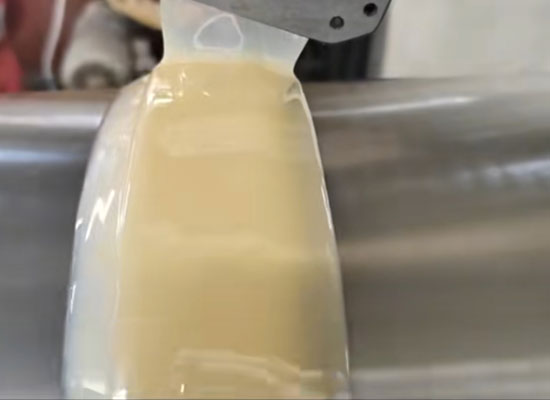

Why Choose Rotational Casting Polyurethane Solutions
- Expertise in custom polyurethane manufacturing with decades of experience.
- Flexibility in design for small prototypes to oversized production parts.
- Strict quality control to ensure strength, consistency, and performance.
- Custom formulations to meet specific hardness, wear, or chemical resistance needs.
- Reliable supply and scalable production to support your industry demands.
Advantages of Rotational Casting Polyurethane
- Uniform wall thickness and consistent material distribution.
- Seamless, void-free parts with excellent structural integrity.
- Ability to produce large or complex hollow components not feasible with other molding methods.
- Cost-effective for low to medium production volumes.
- Design flexibility, allowing for custom shapes, thicknesses, and formulations.
- Durable and chemical-resistant for demanding industrial environments.
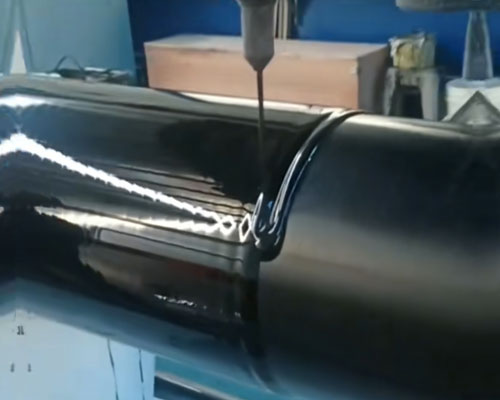
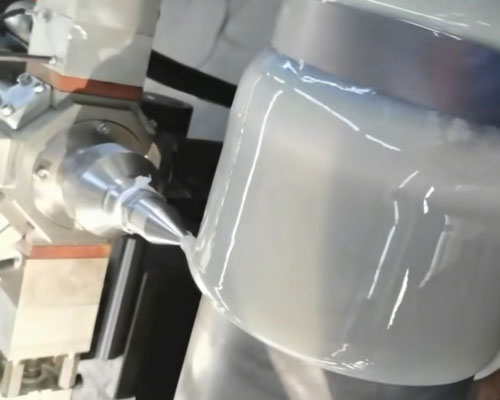


Step-by-Step Rotational Urethane Casting Process
- Mold Preparation – The mold is cleaned, treated with a release agent, and sometimes preheated.
- Material Loading – Liquid polyurethane (or powder for some thermoplastics) is poured into the mold. If making rollers, a metal core can be fixed inside.
- Multi-Axis Rotation – The mold rotates slowly along two or more axes, allowing gravity to distribute the material evenly across the mold’s interior surface.
- Curing – While rotating, the polyurethane cures or solidifies, forming a uniform layer along the mold.
- Demolding – Once fully cured, the part is removed from the mold.
- Finishing – Parts may be trimmed, machined, or surface-treated to achieve tight tolerances or functional finishes.
Case of Rotationally Cast Polyurethane






Applications of Rotomolded Polyurethane
Why Choose Us?
As a trusted custom polyurethane manufacturer, we offer:
- Expertise in rotational casting polyurethane for large, seamless, and durable components.
- End-to-end solutions from design and prototyping to production of oversized parts.
- Uniform, high-strength, and chemically resistant components tailored to your needs.
- Reliable delivery, scalable production, and rigorous quality control for demanding industries.
Contact us today to discuss your rotomolding polyurethane project and see how our custom solutions can improve equipment performance and extend service life.
Rotational Casting (Moldless Casting) Polyurethane Technology is a polyurethane molding method that uses slow, multi-axis rotation to coat the inner walls of a mold with liquid polyurethane. Instead of injecting or compressing material under pressure, this process relies on gravity and continuous rotation to build up uniform layers of polyurethane until the part reaches the desired thickness.
Centrifugal casting uses high-speed, single-axis rotation and centrifugal force, while rotational casting uses slow, multi-axis rotation and gravity for hollow or core-bonded parts.
Hollow components, polyurethane rollers with metal cores, wheels, containers, housings, and large irregularly shaped parts.
Yes. By adjusting rotation speed, mold temperature, and material viscosity, we achieve consistent wall thickness.
Uniform wall thickness, high mechanical strength, seamless construction, customizable properties, and suitability for complex or hollow shapes.
Yes, it is ideal for large or irregular components that are difficult to produce with injection or compression molding.